Understanding "Plastic For Food" is crucial for safety and proper usage. Dr. Jane Thompson, a leading expert in food safety, states, "Not all plastics are created equal." This highlights the complexity of selecting appropriate materials for food contact.
Plastics are prevalent in food packaging and storage. Their versatility and convenience benefit both consumers and manufacturers. However, concerns about chemicals leaching into food persist. Certain plastics contain dangerous additives, causing potential health risks. Labels and guidelines are vital in navigating these choices.
With a multitude of plastic options, it's essential to understand their properties. Not all are safe for every type of food. People often overlook the importance of checking recycling codes. Ignoring these details could lead to harmful consequences. Awareness and education on "Plastic For Food" can help mitigate risks and promote safe practices.
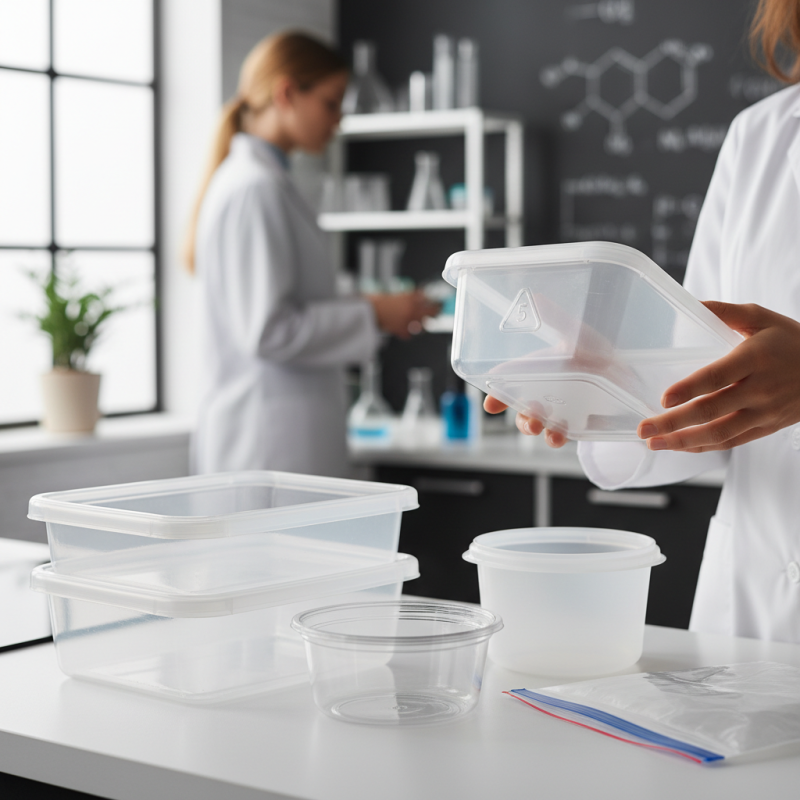

Plastic plays a significant role in food safety. Its versatility makes it a popular choice for packaging and storage. Different types of plastics serve various purposes in our kitchens. However, not all plastics are created equal. Some may leach harmful substances when in contact with food.
Understanding the definition of plastic is crucial. Plastics are synthetic materials made from polymers. They can be flexible or rigid. Commonly used plastics include polyethylene and polypropylene. While these materials are safe for many uses, the potential for chemical migration remains a concern.
Contamination can occur if plastics are not used properly. For instance, heating food in plastic containers may release toxins. It’s essential to read labels and follow usage guidelines. Some plastics are designed for single use only. Ensuring proper disposal is also a consideration for food safety. Awareness of these factors can help in making informed choices.
| Plastic Type | Common Uses | Safety Guidelines | Recycling Code |
|---|---|---|---|
| Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) | Water and soft drink bottles | Generally safe, do not reuse for hot liquids | 1 |
| High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) | Milk jugs, detergent bottles | Safe, suitable for food contact | 2 |
| Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) | Food wraps, bottles | Not recommended for food due to harmful additives | 3 |
| Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE) | Grocery bags, bread bags | Generally safe, not suitable for high heat | 4 |
| Polypropylene (PP) | Microwave containers, yogurt containers | Safe for food contact, microwave safe | 5 |
| Polystyrene (PS) | Disposable cups, plates, food containers | Not recommended due to possible leaching | 6 |
| Other (e.g., polycarbonate) | Reusable water bottles, some container lids | Check for BPA; avoid heating | 7 |

When it comes to food packaging, various types of plastics are commonly used. Polyethylene, for instance, is widely utilized for its flexibility and durability. It's often found in grocery bags and clear food wraps. This plastic can handle different temperatures. However, it may leach chemicals when exposed to high heat.
Polypropylene is another popular choice, particularly for containers and lids. It's known for its resistance to grease and moisture. Many people use polypropylene for lunch boxes. However, it’s essential to ensure that these containers are labeled microwave-safe. Misuse can lead to unwanted chemical absorption.
Polystyrene, often used for foam food containers, offers insulation. It's lightweight and keeps food hot longer. But, concerns about its impact on health and the environment are growing. Not all polystyrene is recyclable, which leads to excess waste. Awareness of these aspects is crucial for making informed choices.
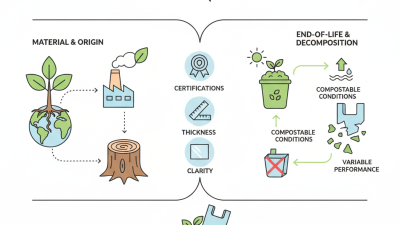
Food-grade plastics are essential in the food supply chain. These materials must meet strict safety standards and regulations. The FDA and the EU have established guidelines to ensure consumer safety. For instance, the FDA states that all food-contact materials must be safe for their intended use. The EU's framework regulation emphasizes that substances must not transfer into food at harmful levels.
A recent report highlighted that over 90% of plastic materials used in food packaging comply with safety requirements. Yet, concerns remain. Some studies indicate that certain food-grade plastics can release chemicals. These chemicals might mimic hormones in the body. This raises questions about long-term health impacts. Reports suggest some food-grade plastics can degrade under high temperatures. Thus, using proper storage conditions is crucial to minimize risks.
Not all food containers are created equal. The recycling process can compromise their safety. Contaminants from previous use may pose risks. Research also shows that consumer awareness is often low. Many do not understand how to check for food-grade certifications. Ensuring food safety involves staying informed and cautious. Choices matter more than ever in a world full of options.
When it comes to food safety, using plastic properly is crucial. According to the FDA, around 90% of households in the U.S. use some form of plastic containers for food storage. However, not all plastics are created equal. Many types can leach harmful chemicals into food, especially when heated. It is vital to check for the recycling code at the bottom of containers. Codes 1, 2, and 5 are generally considered safer options.
While using plastic containers, one must also consider the temperature. For instance, avoid microwaving plastic unless labeled as microwave-safe. High temperatures can break down plastics and release toxins. A study published in the journal "Environmental Science & Technology" noted that chemicals from plastics could disrupt hormones, raising health concerns. To mitigate risks, store food in glass or stainless steel whenever possible.
It’s important not to overlook the wear and tear of plastic containers. Scratches and discoloration can harbor bacteria. Experts recommend replacing plastic containers every few years to ensure safety. Reducing the use of single-use plastics also contributes to environmental health. Consider alternative methods for food storage that protect both your health and the planet.
Plastic is widely used in food packaging and storage. However, concerns about its environmental impact are growing. Many plastics are not biodegradable. They can take hundreds of years to decompose, contributing to pollution crises in oceans and landfills. Wildlife is often harmed when they ingest plastic waste. The sheer volume of plastic used daily is staggering.
As a response to these issues, many alternatives are emerging. Biodegradable materials, such as plant-based containers, are gaining popularity. These options break down more easily in the environment. Reusable containers are also a smart choice; they reduce single-use plastic waste significantly. Yet, not everyone adopts these methods. Some people find it inconvenient to change habits. Awareness is key, but real change takes time and effort.
People often overlook the impact of their choices. A simple decision in food storage can lead to a larger environmental footprint. Educating ourselves about plastic usage is vital. Each small step can contribute to a healthier planet. However, a fundamental shift in behavior is necessary for lasting change.