News

Current Status, Challenges and Green Transformation of Waste Plastic Management
China's waste plastic treatment mainly adopts three methods: landfill, incineration, and recycling. Landfill operations are simple but heavily polluting, and are gradually being replaced; Burning can effectively reduce emissions and generate electricity, but pollutant emissions need to be controlled; Recycling is the most sustainable, but it faces classification and economic challenges. At present, China is building a comprehensive governance system of "reduction recycling disposal", which is promoted through policy guidance, technological innovation, and market mechanisms to achieve a balanced development of plastic pollution control and resource recycling, and to assist in the construction of "waste free cities" and the achievement of dual carbon goals.

Plastics: Innovating for Sustainability, Leading Technological Leaps, and Reshaping a Prosperous Futur-1
Plastics are vital in modern life, from daily bags to industrial parts. The industry has evolved greatly, with new materials and better processes. It focuses on sustainability, with degradable plastics and recycling making progress. Tech brings smart plastics and nanotech applications. The future looks bright, with growing demand and more eco-friendly, intelligent advancements.

The Gift of Plastic: The Invisible Wings of Modern Civilization
In a luxury boutique in Tokyo's Ginza district, a customer receives a high-end purchase packaged in a matte-finish plastic bag. In a remote Kenyan clinic, medical staff retrieve sterile syringes from sealed plastic pouches. At a smart warehouse in Shanghai, anti-static Plastic Bags safeguard delicate microchips awaiting shipment—these seemingly mundane scenes illustrate how plastic bags have quietly become the unsung heroes upholding modern civilization. This article reexamines this often-demonized yet indispensable companion through four dimensions: technological innovation, quality-of-life enhancement, economic contribution, and specialized applications.

Biodegradable Plastic Bags: Technological Breakthroughs and Market Challenges in Environmental Protection
Against the backdrop of an increasingly severe global plastic pollution crisis, biodegradable plastic bags have emerged as an eco-friendly alternative to conventional plastics and are experiencing rapid development. According to data from European Bioplastics, global production capacity of biodegradable plastics reached 2.5 million tons in 2023, with plastic bags accounting for over 40% of applications. This article explores the true potential of this green packaging solution by examining material technologies, degradation mechanisms, and market trends.

Decoding Plastic Bag Manufacturing: A Technical Comparison of LDPE, HDPE, and Biodegradable Materials
Plastic bags have become indispensable in modern daily life, with their manufacturing processes and material selection directly impacting product performance and environmental sustainability. This article provides an in-depth analysis of the production technologies and characteristics of three mainstream plastic bag materials: LDPE, HDPE, and biodegradable alternatives.

The Global Trade and Sustainable Future of Plastic Bags
Plastic bags, as an essential packaging material in modern life, are closely tied to the development of international trade. With the acceleration of globalization, the demand for plastic bags in foreign trade continues to grow, particularly in consumer goods, food packaging, and other sectors. However, environmental concerns and shifting international trade policies also pose challenges for the industry. This article explores the current state of global trade in plastic bags, market drivers, environmental pressures, and future trends, analyzing their role in the global economy and pathways for sustainable transformation.

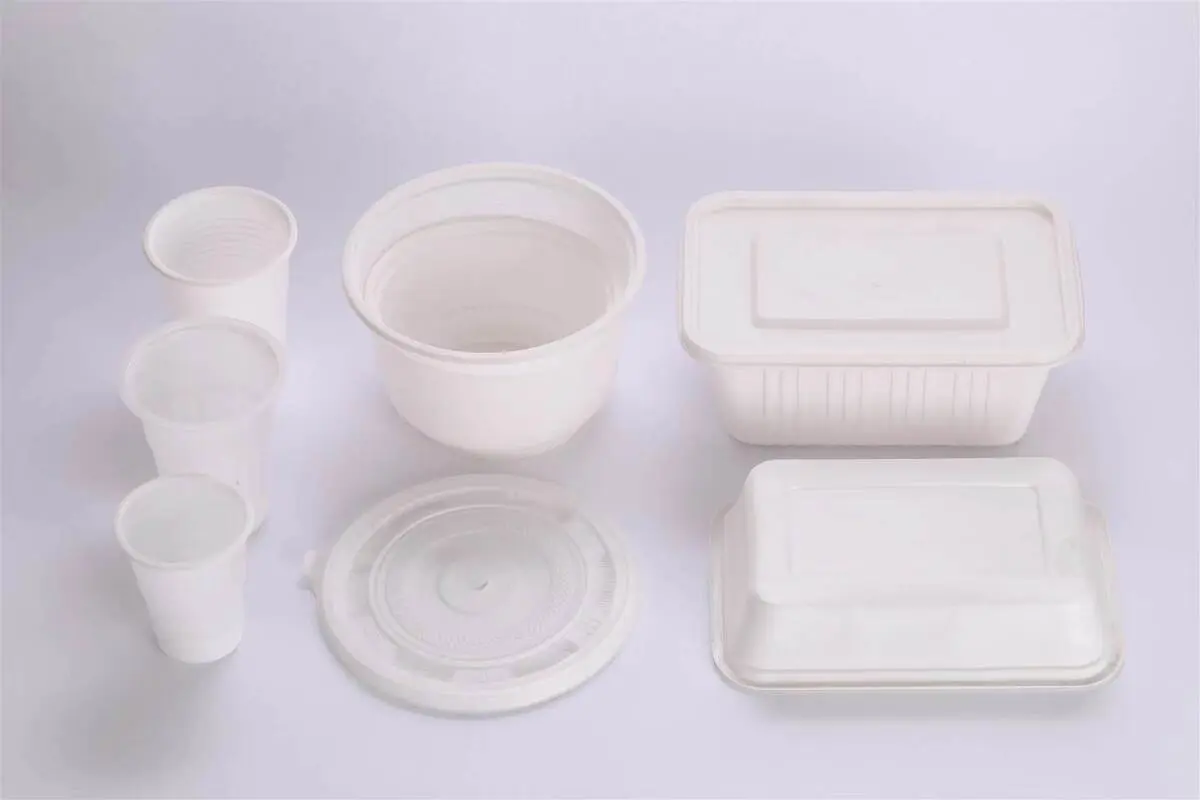
A Comprehensive Guide to Garbage Bags: From Selection to Eco-Friendly Use
Garbage Bags have become an indispensable cleaning product in modern life, widely used in households, offices, property management, and commercial spaces. Their existence has greatly facilitated waste collection and disposal, making environmental sanitation management more efficient. However, faced with the wide variety of garbage bag products on the market, many consumers often feel confused when making purchases. This article will provide a comprehensive guide covering the types, materials, selection techniques, usage considerations, and environmental trends of garbage bags.

The Underrated Benefits of Plastic Bags: A Reassessment of Their Role in Modern Society-1
Plastic bags, often vilified in contemporary environmental discourse, have become a symbol of humanity’s struggle with waste and pollution. Images of floating garbage patches in oceans and entangled wildlife dominate headlines, fueling calls for bans and restrictions. However, this one-sided narrative overlooks the multifaceted advantages plastic bags have offered since their widespread adoption in the mid-20th century. This article aims to provide a balanced perspective by exploring the economic, practical, and even environmental benefits of plastic bags, arguing that their utility should not be dismissed without acknowledging their contributions to human progress.
What is copolymer polyoxymethylene? What are its applications?
Copolymer polyoxymethylene (also known as polyoxymethylene copolymer or polyoxymethylene copolymer) is a high-performance engineering plastic. In addition to repeated -(CH₂O)- segments in the main chain of its molecule, it also contains other copolymer monomer segments (such as ethylene oxide, dioxolane, etc.). Its molecular weight is usually between 20,000 and 40,000. It has excellent comprehensive properties, such as high mechanical strength, fatigue resistance, creep resistance, low friction coefficient, chemical corrosion resistance, etc. It is called "super steel" or "steel", and can partially replace metal materials such as copper, aluminum, and zinc.
World's First "Reed-to-Plastic" Production Line Begins Operation, Capable of Producing Polylactic Acid
Recently, the world's first polylactic acid (PLA) production line using reeds as raw material officially commenced operations. The facility consumes approximately 50 tons of reeds, straw, and other raw materials daily, producing around 10 tons of PLA and lignin. This production line was invested in and constructed by a Chinese company, whose independently developed production technology is internationally leading, successfully filling the gap in non-food-based bioplastics.